Zhaoxian Wu
Ph.D. student in
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Cornell University and Cornell Tech
E-mail: zw868 [@] cornell [.] edu
Address: 2 W Loop Rd, New York, NY, 10044
About me
I am currently pursuing my Ph.D. degree in Electrical and Computer Engineering at Cornell University, based at the Cornell Tech Campus in New York City, fortunately advised by Prof. Tianyi Chen. Prior to that, I have spent two years at the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and transferred with my advisor. I received the bachelor's and master's degree from Sun Yat-sen University under the supervision of Prof. Qing Ling.
Education
- 2025 – present Ph.D., Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University New York, NY
- 2023 – 2025 Ph.D., Electrical, Computer, and Systems Engineering, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Troy, NY
- 2020 – 2023 M.E., Computer Science, Sun Yat-sen University Guangzhou, China
- 2016 – 2020 B.E., Software Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University Guangdong, China
Research
My research interest lies in Analog In-memory Computing, and optimization theory.
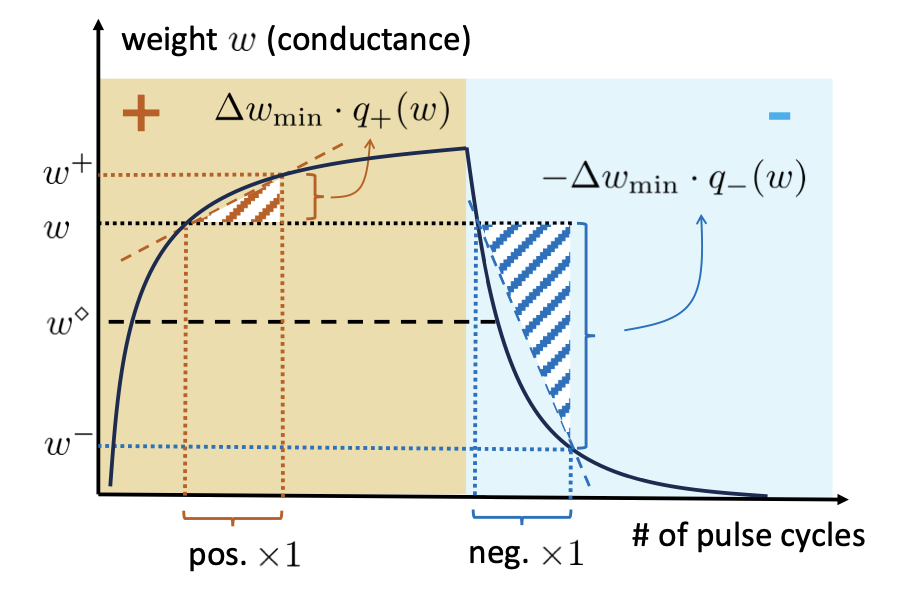
Modern deep model training often requires processing vast amounts of weights and data, which necessitates frequent data transfer between memory and processor, leading to the "von Neumann bottleneck" that can significantly hinder computation speed and efficiency. In this context, Analog in-memory computing (AIMC) emerges as an innovative computing paradigm that utilizes the physical properties of emerging Resistive Processing Unit (RPU) devices to perform computations directly within memory arrays. Its core principle is to harness the analog storage and processing capabilities of these devices—leveraging the physical laws of Ohm and Kirchhoff—to execute Matrix-Vector Multiplication (MVM) operations in a highly parallel and energy-efficient manner.
To fully realize the massive parallelism and energy efficiency benefits of AIMC, it is essential to perform the fully on-chip AI model training directly on the AIMC hardware. However, this ambitious goal faces significant challenges stemming from the inherent non-idealities of analog hardware. Key difficulties include the non-linear response of RPU devices, the pervasive presence of analog noise during computation, and the limited precision inherent in analog operations. Achieving the high accuracy required for training deep models, especially given these imperfections, remains a formidable obstacle.
Crucially, since these hardware imperfections, such as device non-linearities and analog noise, are fundamentally physical and cannot be entirely eliminated in the foreseeable future, algorithmic solutions become essential. To address this reality, my research focuses on developing novel algorithms and techniques that enable the effective model training on AIMC hardware. Our core objective is to establish a robust training paradigm that enables AI models to seamlessly "coexist" with the intrinsic imperfections of analog accelerators. Specifically, we aim to develop algorithms that are inherently robust against hardware imperfections, ultimately bridging the gap between the computational demands of DNNs and the realities of non-ideal analog in-memory accelerators.
News
Publications
For the most up-to-date list of publications, please visit my Google Scholar
 NeurIPS (Oral)
NeurIPS (Oral)
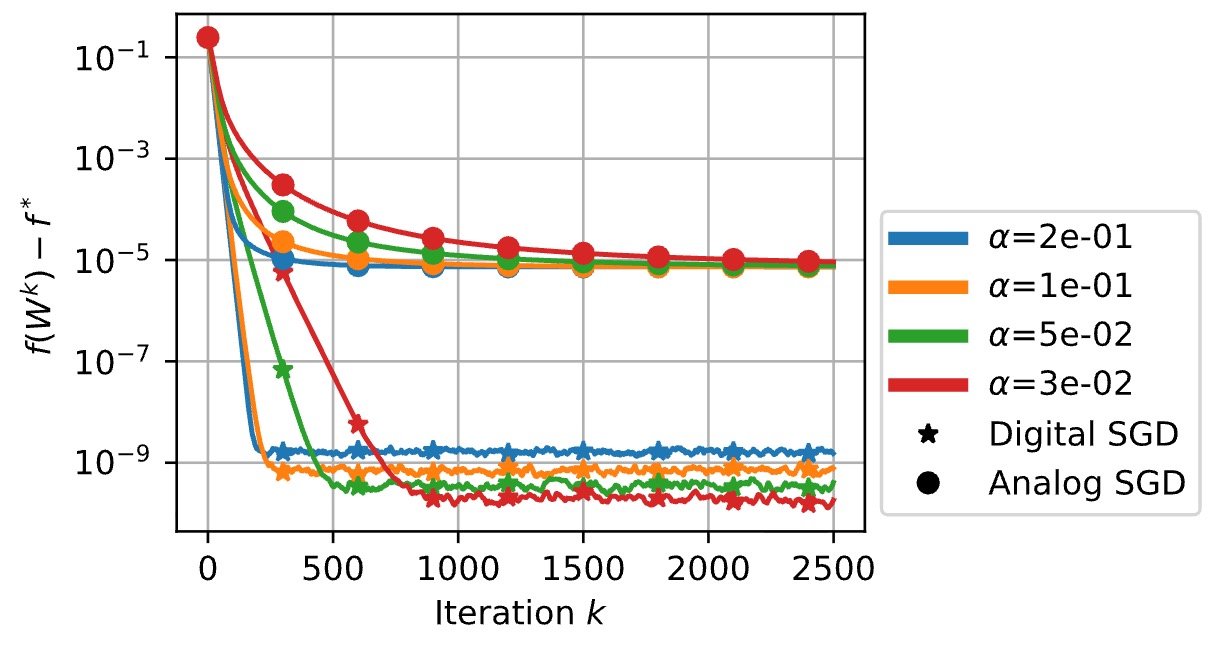
Analog In-memory Training on General Non-ideal Resistive Elements: The Impact of Response Functions
Zhaoxian Wu, Quan Xiao, Tayfun Gokmen, Omobayode Fagbohungbe, and Tianyi Chen
Proc. of Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025.
Oral, top 0.3% of all submissions
 NeurIPS
NeurIPS
Towards Exact Gradient-based Training on Analog In-memory Computing
Zhaoxian Wu, Tayfun Gokmen, Malte J. Rasch, Tianyi Chen
Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024.
 TSP
TSP
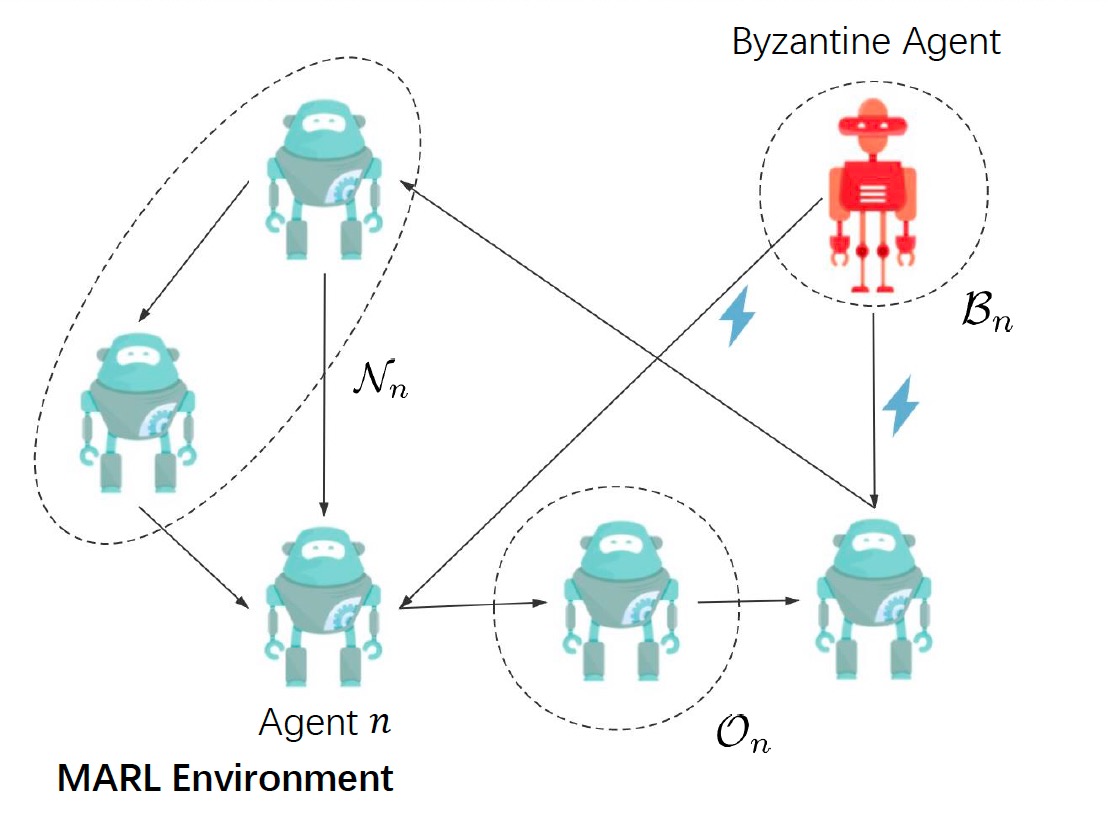
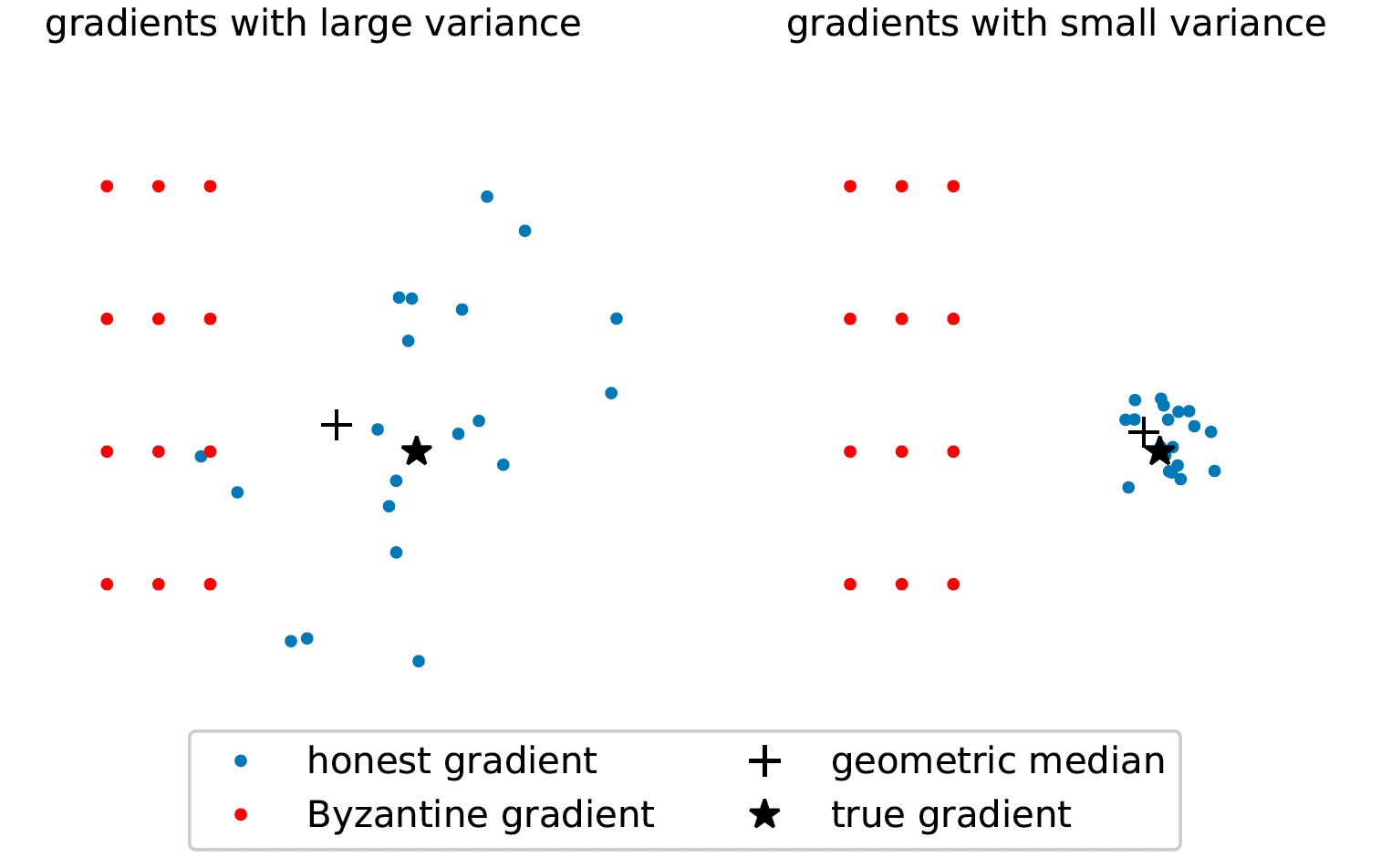
Byzantine-Resilient Decentralized Stochastic Optimization with Robust Aggregation Rules
Zhaoxian Wu, Tianyi Chen, Qing Ling
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP), 2023.
 TSP
TSP
Byzantine-resilient Decentralized Policy Evaluation with Linear Function Approximation
Zhaoxian Wu, Han Shen, Tianyi Chen, Qing Ling
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP), 2021.
 TSP
TSP
Federated Variance-reduced Stochastic Gradient Descent with Robustness to Byzantine Attacks
Zhaoxian Wu, Qing Ling, Tianyi Chen, and Georgios B Giannakis
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP), 2020.
IEEE SPS Young Author Best Paper Award
 NeurIPS (Oral)
NeurIPS (Oral)
Analog In-memory Training on General Non-ideal Resistive Elements: The Impact of Response Functions
Zhaoxian Wu, Quan Xiao, Tayfun Gokmen, Omobayode Fagbohungbe, and Tianyi Chen
Proc. of Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025.
Oral, top 0.3% of all submissions
 TPAMI
TPAMI
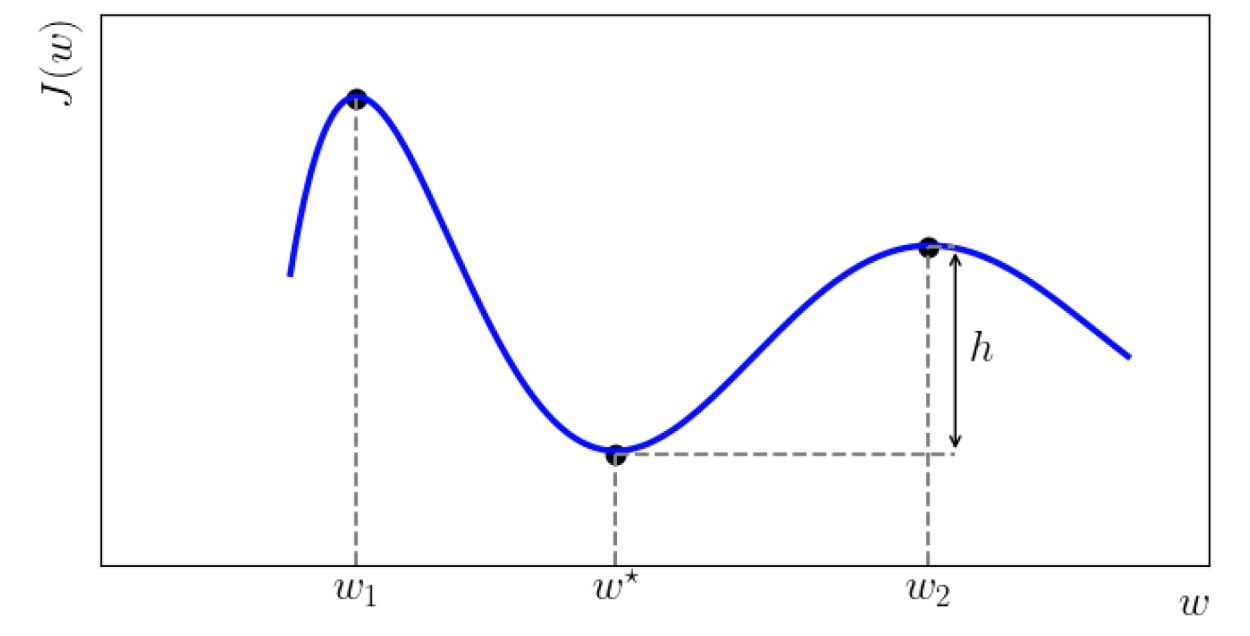
On the Trade-Off Between Flatness and Optimization in Distributed Learning
Ying Cao, Zhaoxian Wu, Kun Yuan, Ali H. Sayed
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2025.
 TSP
TSP
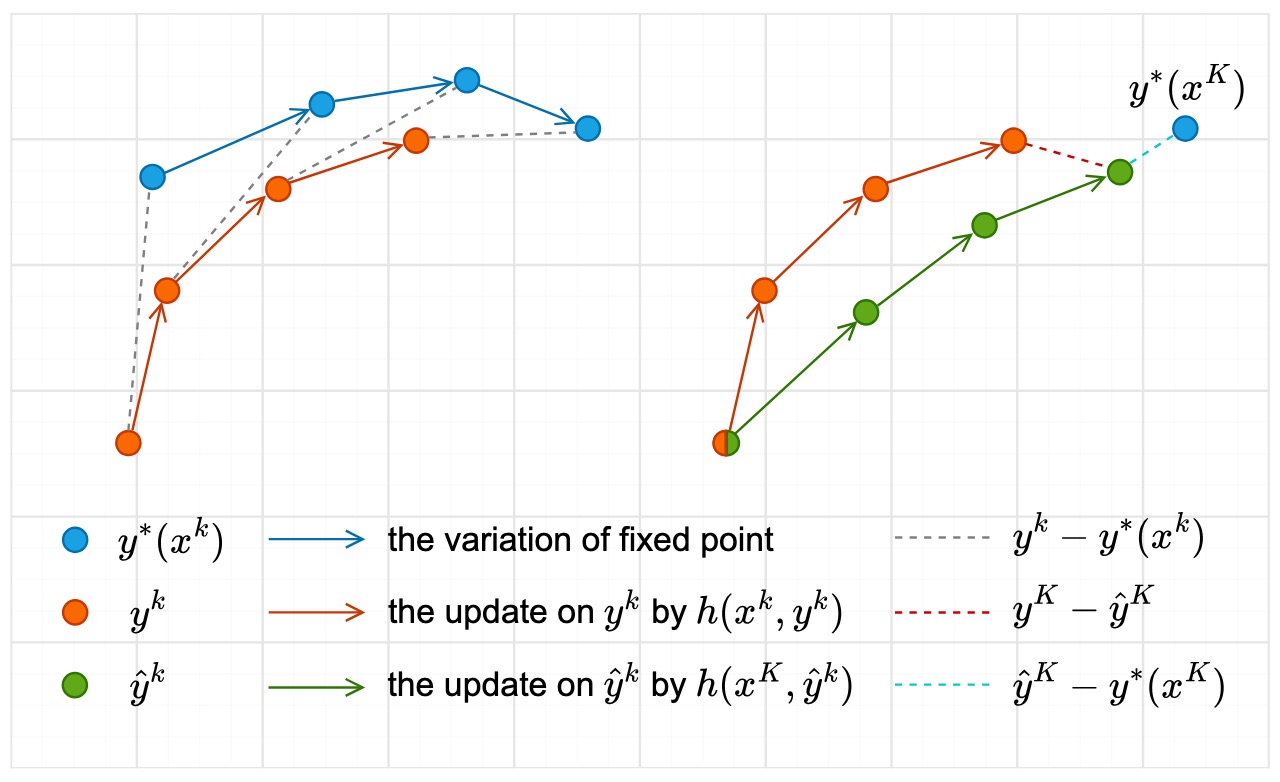
Single-Timescale Multi-Sequence Stochastic Approximation Without Fixed Point Smoothness: Theories and Applications
Yue Huang, Zhaoxian Wu, Shiqian Ma, Qing Ling
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP), 2025.
 NeurIPS
NeurIPS
Towards Exact Gradient-based Training on Analog In-memory Computing
Zhaoxian Wu, Tayfun Gokmen, Malte J. Rasch, Tianyi Chen
Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024.
 TSP
TSP
Byzantine-Robust Distributed Online Learning: Taming Adversarial Participants in An Adversarial Environment
Xingrong Dong, Zhaoxian Wu, Qing Ling, Zhi Tian
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP), 2024.
 TSP
TSP
Byzantine-Resilient Decentralized Stochastic Optimization with Robust Aggregation Rules
Zhaoxian Wu, Tianyi Chen, Qing Ling
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP), 2023.
 Info. Sci.
Info. Sci.
Byzantine-Robust Variance-Reduced Federated Learning over Distributed Non-i.i.d. Data
Jie Peng, Zhaoxian Wu, Qing Ling
Information Sciences, 2022.
 TNNLS
TNNLS
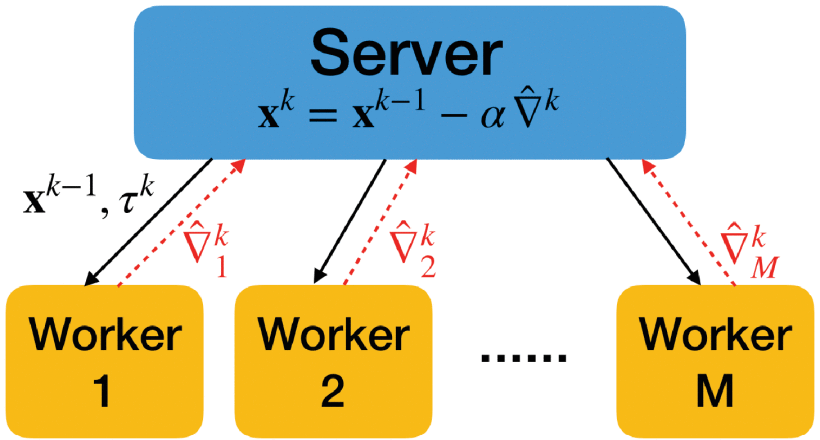
Communication-censored Distributed Stochastic Gradient Descent
Weiyu Li, Zhaoxian Wu, Tianyi Chen, Liping Li, Qing Ling
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (TNNLS), 2021.
 TSP
TSP
Byzantine-resilient Decentralized Policy Evaluation with Linear Function Approximation
Zhaoxian Wu, Han Shen, Tianyi Chen, Qing Ling
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP), 2021.
 TSP
TSP
Federated Variance-reduced Stochastic Gradient Descent with Robustness to Byzantine Attacks
Zhaoxian Wu, Qing Ling, Tianyi Chen, and Georgios B Giannakis
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP), 2020.
IEEE SPS Young Author Best Paper Award
 ICASSP
ICASSP
On the Convergence of Single-Timescale Multi-Sequence Stochastic Approximation Without Fixed Point Smoothness
Yue Huang, Zhaoxian Wu, Qing Ling
International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2024.
 ICASSP
ICASSP
Distributed Online Learning With Adversarial Participants In An Adversarial Environment
Xingrong Dong, Zhaoxian Wu, Qing Ling, Zhi Tian
International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2023.
 ICASSP
ICASSP
A Byzantine-resilient Dual Subgradient Method for Vertical Federated Learning
Kun Yuan, Zhaoxian Wu, Qing Ling
International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2022.
 ICASSP
ICASSP
Byzantine-resilient Decentralized TD Learning with Linear Function Approximation
Zhaoxian Wu, Han Shen, Tianyi Chen, Qing Ling
International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2021.
 ICASSP
ICASSP
Byzantine-resilient Distributed Finite-sum Optimization over Networks
Zhaoxian Wu, Qing Ling, Tianyi Chen, and Georgios B Giannakis
International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2020.
Experience
- Student Volunteer for Cornell ECE 5290/7290 & ORIE 5290: Distributed Optimization for Machine Learning and AI, Fall 2025
- Guest Lecturer for RPI ECSE-4964/6964 Distributed Optimization & Machine Learning, Spring 2025
- Reviewer of NeurIPS (2025)
- Reviewer of IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing
- Reviewer of IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks
- Reviewer of IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control
- Reviewer of IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology
- Reviewer of IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems
- Reviewer of IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security
- Reviewer of Signal Processing
- Reviewer of IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory
- Reviewer of American Control Conference
Awards & Honors
- IEEE Signal Processing Society Scholarship, 2025
- IEEE Signal Processing Society Young Author Best Paper Award, 2024
- China Institute of Electronics Master's Thesis Incentive Program (2023)
- National Academic Scholarship, 2017
- Outstanding Undergraduate Thesis in SYSU, 2020
- Outstanding Paper at Graduate Student Forum of The Mathematical Programming Branch of Operations Research Society of China, 2021
- ICASSP travel grant, 2020
